Exploring the Fascinating Landscape of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico: A Detailed Map Guide
Introduction
map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico, with its rich history, vibrant culture, and diverse geography, has long fascinated travelers, historians, and geographers alike. When people think of Mexico, they often picture its stunning beaches, ancient ruins, and bustling cities. However, the map of Mexico reveals much more—a tapestry of mountains, deserts, forests, and coastlines that contribute to the country’s natural beauty and unique identity.
In this article, we will dive into the details of the landscape, geography, and key regions of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico. We’ll explore the country’s rich terrain, prominent cities, cultural significance, and natural resources, all while giving you a virtual tour using the map as our guide. Whether you’re planning a trip or are just curious about Mexico, this detailed look at the map will give you a fresh perspective on this incredible country.
Understanding map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico

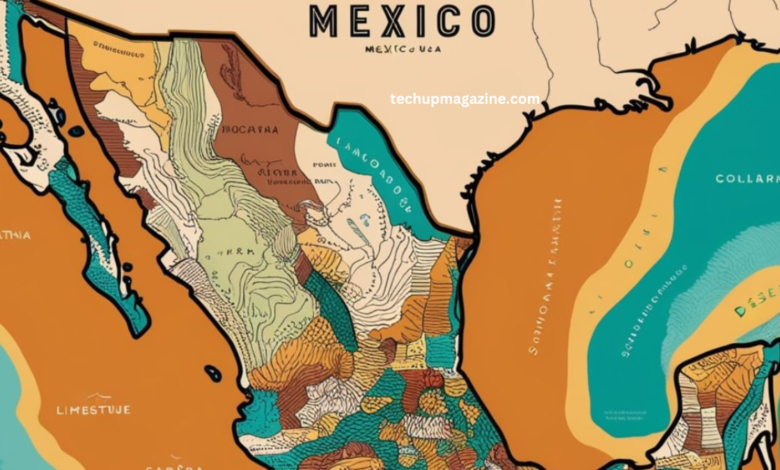
map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico in North America, bordered by the United States to the north, Guatemala, and Belize to the southeast, and flanked by the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Its geography is remarkably diverse, offering a variety of landscapes that include arid deserts, lush rainforests, volcanic mountain ranges, and tropical coastlines.
The northern region of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico is characterized by vast deserts such as the Sonoran and map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico. These deserts, while harsh, are home to a surprising amount of biodiversity. The central part of Mexico is dominated by the Sierra Madre mountain ranges, offering fertile lands for agriculture and breathtaking views. In contrast, the southern regions feature tropical rainforests and some of the most biologically diverse ecosystems in the world.
Understanding the geography of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico is key to appreciating the cultural and environmental richness that the country offers. Each region has its distinct climate, resources, and way of life, all of which can be traced back to the map.
The Northern Deserts: Sonoran and Chihuahuan
The northern deserts of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico are vast, arid regions that may initially seem desolate, but they are anything but lifeless. The Sonoran Desert, for example, is known for its unique plant life, including the iconic saguaro cactus. This desert spans parts of both Mexico and the United States, stretching into the states of Sonora and Baja California in Mexico. The Chihuahuan Desert, located in the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Durango, is equally expansive and home to a variety of endemic species of plants and animals.
Life in these deserts is challenging, but many indigenous cultures have thrived here for centuries. The deserts are also home to some of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico most significant archaeological sites, remnants of ancient civilizations that once ruled these lands. Despite their harsh climates, these deserts have a certain beauty that can only be appreciated by spending time in their solitude.
From a geographical standpoint, the northern deserts of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico are a key part of the country’s landscape. Their vastness and stark beauty are reflected on the map, which shows them stretching across large portions of the northern half of the country.
The Sierra Madre Mountains
map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico central region is dominated by the Sierra Madre mountain ranges, which play a crucial role in shaping the country’s geography. These ranges consist of the Sierra Madre Occidental, running along the western side of Mexico, and the Sierra Madre Oriental, running parallel along the eastern side. Together, these mountains form the spine of the country and are responsible for much of the climate variation in the regions they traverse.
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a rugged, volcanic range that provides map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico with some of its most dramatic landscapes, including towering cliffs, deep canyons, and vast plateaus. The range is also home to the famous Copper Canyon (Barranca del Cobre), a natural wonder that is even deeper than the Grand Canyon in the United States. This area is rich in biodiversity and is considered a prime spot for eco-tourism.
The Sierra Madre Oriental, on the other hand, is less volcanic but just as imposing. It is home to rich forests, waterfalls, and deep gorges that attract nature lovers and adventurers. These mountain ranges not only define the physical landscape of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexicobut also influence the culture and economy of the regions through which they pass. The fertile valleys between the mountains are some of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico most important agricultural areas, providing food for much of the country.
The Central Plateau
The Central Plateau, also known as the Mexican Plateau, lies between the Sierra Madre mountain ranges and covers a significant portion of the country. This area is considered one of the most important geographical regions of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico, both historically and economically. The plateau is characterized by its high elevation, with many areas sitting at over 2,000 meters above sea level, making it one of the highest plateaus in the world.
The climate in this region is typically temperate, with cool winters and warm summers, which makes it ideal for agriculture. The Central Plateau has historically been the heart of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico agricultural output, producing crops such as maize, beans, and wheat. Additionally, the plateau is home to many of Mexico’s largest cities, including the capital, map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico City, which is nestled in a valley at the southern end of the plateau.
The plateau is also a cultural hub, with many of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico indigenous groups having originated from this area. The Aztecs, one of the most well-known civilizations in the history of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico, established their capital, Tenochtitlan, on the Central Plateau. Today, the remnants of this ancient civilization can still be seen in the archaeological ruins that dot the region.
The Gulf Coast and Eastern Lowlands
The eastern side of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico is bordered by the Gulf of Mexico, and this region is known for its warm climate, lush vegetation, and fertile soils. The Gulf Coast is a key area for map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico economy, as it is home to the country’s largest oil reserves and many of its key ports. The state of Veracruz, for example, is known for its rich natural resources, including oil, natural gas, and agricultural products such as sugarcane and coffee.
The region also has a rich cultural history, with the ancient Olmec civilization having once thrived here. The Olmecs are considered one of the earliest civilizations in the Americas, and their influence can still be seen in the art, culture, and architecture of the region today.
The Gulf Coast is also home to some of map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico most beautiful beaches and natural reserves, making it a popular tourist destination. The lush jungles and tropical forests that line the coast are home to a variety of wildlife, including jaguars, monkeys, and a diverse array of bird species.
The Yucatan Peninsula
The Yucatan Peninsula, located in southeastern map:danhyf_d1wi= mexico, is one of the most famous and recognizable regions of the country, thanks to its unique geology and rich cultural history. The peninsula is largely flat and is composed of limestone, which has resulted in the formation of thousands of cenotes, or natural sinkholes, that are scattered across the region. These cenotes were sacred to the ancient Maya civilization, and many are still used today for swimming and diving.
The Yucatan Peninsula is home to some of Mexico’s most iconic archaeological sites, including Chichen Itza, Uxmal, and Tulum. These ancient Mayan cities attract millions of tourists each year, who come to marvel at the pyramids, temples, and palaces that have stood for centuries.
In addition to its cultural significance, the Yucatan Peninsula is known for its stunning coastline along the Caribbean Sea. The beaches of Cancun, Playa del Carmen, and Tulum are among the most popular tourist destinations in the world, offering crystal-clear waters, white sandy beaches, and a wealth of recreational activities.
Mexico City: The Capital and Heart of the Nation
Mexico City, the capital of Mexico, is one of the largest and most vibrant cities in the world. Located in the Valley of Mexico, a high-altitude basin on the Central Plateau, Mexico City is not only the political and economic hub of the country but also a cultural and historical center.
The city is built on the ruins of Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Aztec Empire, and traces of this ancient civilization can still be found in the city’s architecture, museums, and archaeological sites. The city is a fascinating blend of old and new, where colonial-era buildings stand alongside modern skyscrapers, and traditional markets coexist with high-end shopping centers.
Mexico City is also known for its rich cultural scene, offering everything from world-class museums and theaters to street art and music. The city’s vibrant food scene is another major draw, with everything from traditional Mexican street food to high-end international cuisine available at every turn.
Geographically, Mexico City is surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, including the famous Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl. The city’s high elevation and valley location give it a unique climate, with mild temperatures year-round but occasional bouts of air pollution due to its enclosed geography.
Baja California Peninsula
The Baja California Peninsula, located in northwestern Mexico, is a long, narrow strip of land that stretches down from the US-Mexico border to the Pacific Ocean. The peninsula is known for its dramatic landscapes, which include rugged mountains, desert plains, and beautiful coastlines. The Sea of Cortez, which lies between the peninsula and the mainland, is often referred to as the “aquarium of the world” due to its rich marine biodiversity.
The Baja California Peninsula is a popular destination for adventure tourism, offering opportunities for hiking, camping, and off-roading. The region is also famous for its whale-watching, as many species of whales migrate to the warm waters of the Sea of Cortez during the winter months.
Culturally, Baja California has a unique blend of Mexican and American influences, due in part to its proximity to the United States. The region is also known for its wine production, with the Valle de Guadalupe being one of the most important wine-producing areas in Mexico.
The Southern Rainforests
Southern Mexico is home to some of the most biodiverse rainforests in the world, particularly in the states of Chiapas and Oaxaca. These rainforests are rich in both plant and animal life, providing a habitat for jaguars, tapirs, howler monkeys, and a variety of bird species. The region is also home to numerous indigenous communities, many of whom have lived in harmony with the rainforest for centuries.
The rainforests of southern Mexico are not only important for biodiversity but also for their cultural significance. Many ancient civilizations, including the Maya and the Zapotecs, once thrived in this region. Today, the ruins of cities such as Palenque, Monte Alban, and Mitla can be explored, offering a glimpse into the past.
These rainforests are under threat from deforestation and agricultural expansion, but efforts are being made to preserve this vital ecosystem. Ecotourism has become an important industry in the region, offering travelers the chance to experience the beauty of the rainforest while contributing to its conservation.
The Pacific Coast
The Pacific Coast of Mexico is known for its stunning beaches, dramatic cliffs, and vibrant coastal towns. This region is a popular destination for surfers, sun-seekers, and adventure travelers, offering everything from world-class waves to hidden coves and quiet fishing villages.
Some of the most famous destinations along the Pacific Coast include Puerto Vallarta, Acapulco, and Mazatlán. Each of these cities has its unique charm, with a mix of traditional Mexican culture and modern tourist amenities.
The Pacific Coast is also known for its vibrant marine life, including sea turtles, dolphins, and whales. Many of the beaches in this region serve as nesting grounds for sea turtles, and conservation efforts have been put in place to protect these endangered species.
In addition to its natural beauty, the Pacific Coast is home to several important historical and cultural sites. The city of Oaxaca, located inland from the coast, is known for its rich indigenous culture and vibrant art scene, while the town of Tequila, located further north, is the birthplace of Mexico’s most famous spirit.
Conclusion
The map of Mexico reveals a country of incredible geographical diversity, with each region offering its unique landscapes, cultures, and experiences. From the deserts of the north to the rainforests of the south, and from the bustling streets of Mexico City to the quiet beaches of the Pacific Coast, Mexico is a country that truly has something for everyone.
Exploring Mexico through its map allows us to appreciate the vastness and complexity of this remarkable country. Whether you’re drawn to its natural beauty, rich history, or vibrant culture, Mexico offers endless opportunities for exploration and discovery.



